Home » Chronic Sinusitis
Chronic sinusitis is a condition in which the spaces inside the nose and head are swollen and inflamed for three months or longer. This condition may be caused by an infection, growths in the sinuses or swelling of the lining of the sinuses.
Common symptoms of chronic sinusitis include:
Because chronic sinusitis and acute sinusitis have similar symptoms, it’s important to understand that acute sinusitis is a temporary sinus infection often associated with a cold. Chronic sinusitis, however, lasts at least 12 weeks.
Left untreated, chronic sinusitis may lead to vision problems (either reduced vision or blindness that may become permanent), inflammation of the membranes and fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord, serious skin infection or an infection in the bones.
Chronic sinusitis may be caused by nasal polyps, a deviated nasal septum, allergies, respiratory tract infections or other medical conditions.
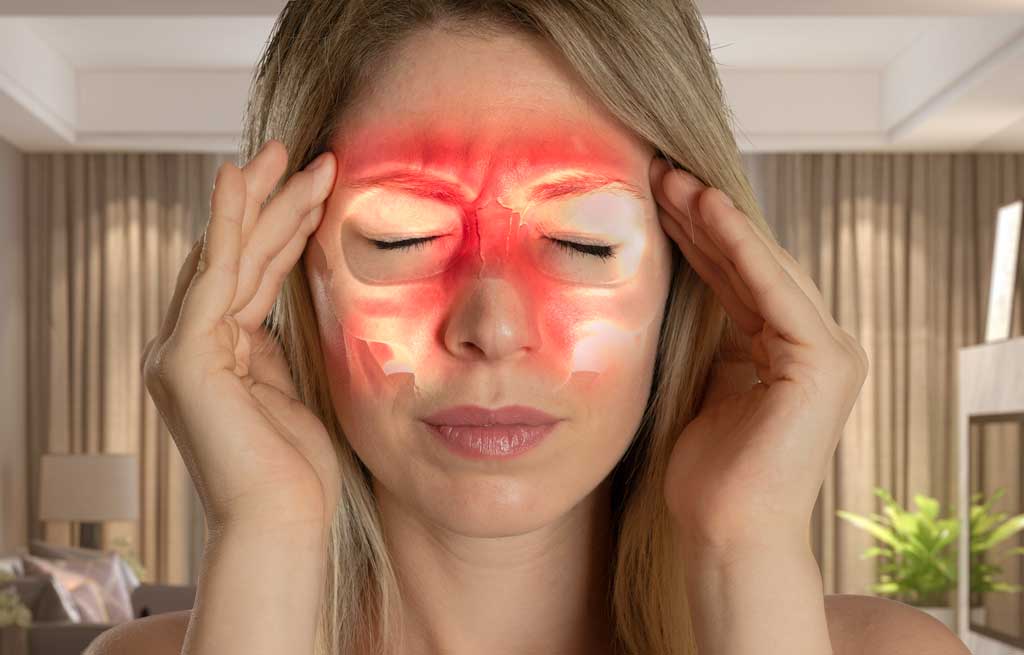

The following factors may increase an individual’s risk of developing chronic sinusitis:
To reduce the risk of chronic sinusitis, individuals should:
Individuals should schedule an appointment with their doctor if they:
It’s important to seek immediate medical attention if individuals are experiencing the following symptoms:
During the visit, the physician will feel the patient’s nose and face for tenderness, and use an endoscope to observe the patient’s sinuses. If the physician suspects an allergy, they will recommend an allergy skin test to identify the allergen causing nasal flare-ups. An imaging test, such as a CT or MRI scan, may be used to pinpoint a deep inflammation or physical obstruction.