Home » Nasal Turbinate Reduction

The turbinates may become enlarged as a result of:
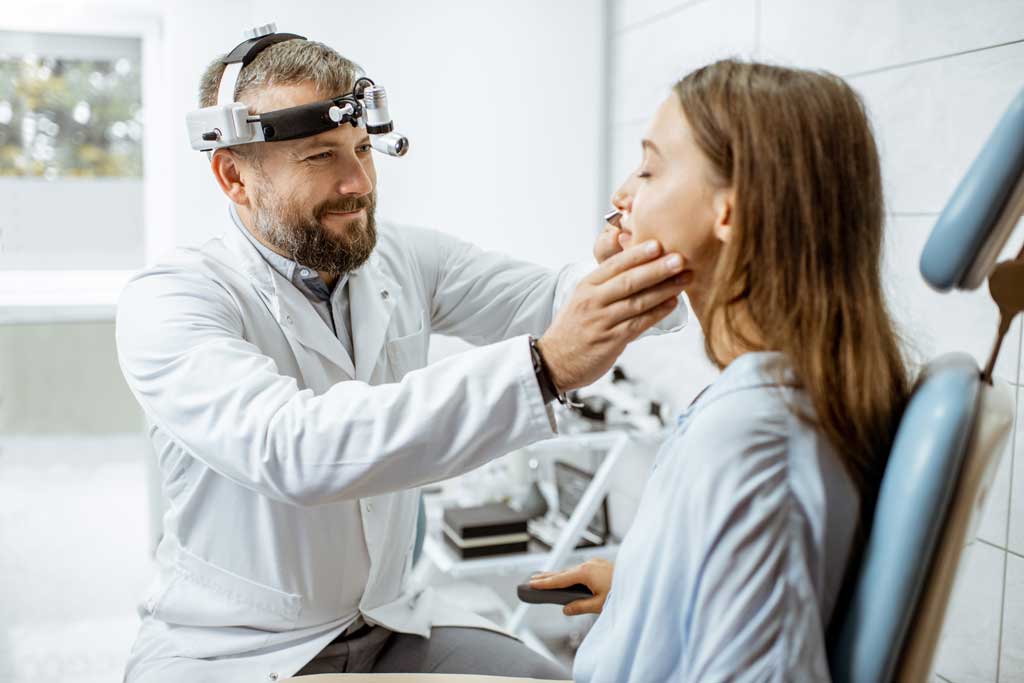
Turbinate reduction may be necessary for individuals who have undergone septoplasty, a procedure done to correct a deviated septum. A turbinate reduction may also be recommended for individuals with enlarged turbinates, or turbinate hypertrophy.
For less severe cases, turbinate reduction is performed under local anesthesia and takes about 10 minutes. The doctor will begin the procedure by using a needle to inject anesthesia into the nasal tissue. Next, the doctor will use a needle-like device to heat the turbinates using a heat source or energy waves. The heat will cause scar tissue to form and reduce the size of the turbinates.
Individuals with significantly enlarged turbinates may require surgical removal. The patient will be under general anesthesia and the surgery will be performed in an operating room. Once the patient has been sedated, the surgeon will use an endoscope to improve visualization during surgery. They will then make an incision in the lining mucosa of the turbinate and remove the underlying bone of the turbinate. Or, the surgeon may use a microdebrider to thin the tissue around the turbinate. Another option would be to use radio frequency waves or an electrical current.
The procedure is relatively safe with few complications that may include bleeding, dryness, crusting, and scarring. Patients may use a saline spray solution to improve dryness and speed up the recovery process.
Side effects for more invasive turbinate reduction procedures include:
Some patients may have turbinates regrow after surgery and require further turbinate reduction treatment.