Sleep Apnea Surgery
Sleep apnea is a condition that causes breathing to periodically stop during sleep. Patients with this condition may need sleep apnea surgery to alleviate symptoms.
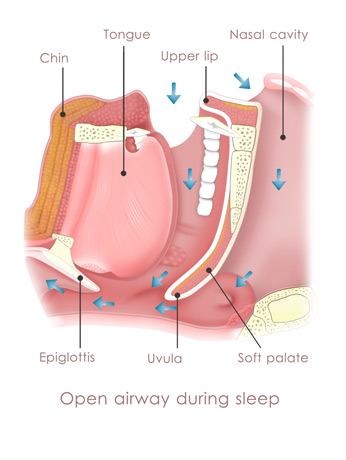
There are three main types of sleep apnea: In obstructive sleep apnea, the throat muscles relax. In central sleep apnea, the brain fails to send the proper signals to the muscles responsible for breathing. Complex sleep apnea syndrome is a combination of the other two types of sleep apnea.
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Patients may have sleep apnea if they are experiencing the following symptoms:
Sleep Apnea Surgery Options
Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition, the physician may recommend one of the following procedures: radiofrequency volumetric tissue reduction, uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, maxillomandibular advancement, anterior inferior mandibular osteotomy, genioglossus advancement, midline glossectomy and base of tongue reduction, lingual tonsillectomy, septoplasty and turbinate reduction, hypoglossal nerve stimulator, or hyoid suspension.

Contact Us Today
The Risks and Risk Factors of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea may increase an individual’s risk of developing high blood pressure, metabolic conditions and other health issues.
Individuals may be at greater risk of developing sleep apnea if they:
Are obese
Have a thick neck
Have a narrowed airway
Are male
Are older
Have a family history of sleep apnea
Smoke
Use alcohol, sedatives or tranquilizers
Have nasal congestion
Have other medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, congestive heart failure, type 2 diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, hormonal disorders, chronic lung disease, and polycystic ovary syndrome
Have had a stroke
Use narcotic pain medications
Have heart disorders








